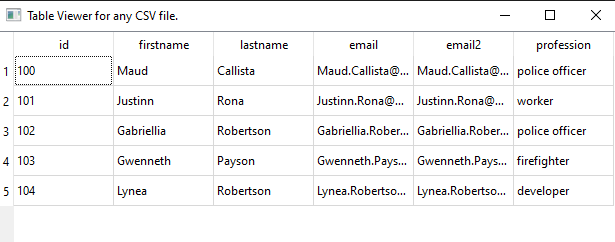
The python language was mainly developed to emphasis on code readability.
That's why I think that it should not be affected by such errors, but they are easily fixed ...
launcher = self._get_launcher('t')
File "C:\Users\catafest\AppData\Roaming\Python\Python37\site-packages\pip\_vendor\distlib\scripts.py", line 404, in _get_launcher
raise ValueError(msg)
ValueError: Unable to find resource t64.exe in package pip._vendor.distlib
[notice] A new release of pip available: 22.3 -> 22.3.1
[notice] To update, run: python.exe -m pip install --upgrade pip
C:\PythonProjects\scapy001>python -m pip uninstall pip setuptools
Found existing installation: pip 22.3
Uninstalling pip-22.3:
Would remove:
c:\users\catafest\appdata\roaming\python\python37\scripts\pip.exe
c:\users\catafest\appdata\roaming\python\python37\scripts\pip3.10.exe
c:\users\catafest\appdata\roaming\python\python37\scripts\pip3.7.exe
c:\users\catafest\appdata\roaming\python\python37\scripts\pip3.exe
c:\users\catafest\appdata\roaming\python\python37\site-packages\pip-22.3.dist-info\*
c:\users\catafest\appdata\roaming\python\python37\site-packages\pip\*
Proceed (Y/n)? y
Successfully uninstalled pip-22.3
Found existing installation: setuptools 47.1.0
Uninstalling setuptools-47.1.0:
Would remove:
c:\python379\lib\site-packages\easy_install.py
c:\python379\lib\site-packages\pkg_resources\*
c:\python379\lib\site-packages\setuptools-47.1.0.dist-info\*
c:\python379\lib\site-packages\setuptools\*
c:\python379\scripts\easy_install-3.7.exe
c:\python379\scripts\easy_install.exe
Proceed (Y/n)? y
Successfully uninstalled setuptools-47.1.0
C:\PythonProjects\scapy001>pip3 install --upgrade pip
Requirement already satisfied: pip in c:\python379\lib\site-packages (22.3.1)
C:\PythonProjects\scapy001>pip install --upgrade setuptools
Collecting setuptools
Downloading setuptools-65.6.3-py3-none-any.whl (1.2 MB)
---------------------------------------- 1.2/1.2 MB 4.1 MB/s eta 0:00:00
Installing collected packages: setuptools
Successfully installed setuptools-65.6.3