
Is a blog about python programming language. You can see my work with python programming language, tutorials and news.
Saturday, October 18, 2025
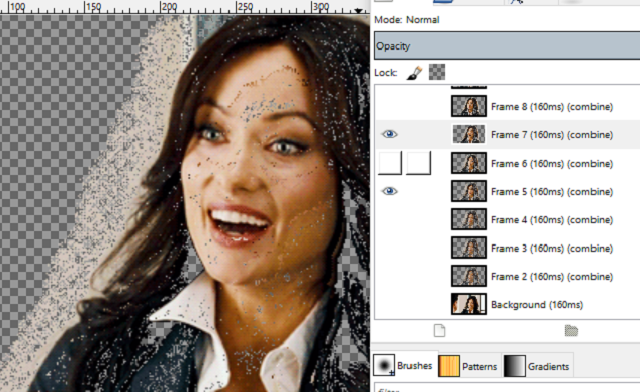
Python Qt6 : tool for cutting images ...

Saturday, July 12, 2025
Python Qt6 : simple merge sprites images with unittest feature.
import os
import unittest
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont, ImageQt
import shutil
from PyQt6.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QPushButton, QFileDialog, QLabel, QVBoxLayout, QWidget, QComboBox
from PyQt6.QtGui import QPixmap
from PyQt6.QtCore import Qt
import sys
def create_test_image(path, size, number):
img = Image.new('RGBA', size, (255, 255, 255, 255))
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
# Simplified to just draw the number with a basic color background
draw.rectangle((0, 0, size[0], size[1]), fill=(0, 100 * number % 255, 0, 255))
try:
font = ImageFont.load_default()
except:
font = None
draw.text((size[0]//2-5, size[1]//2-5), str(number), fill=(255, 255, 255, 255), font=font)
img.save(path, 'PNG')
def merge_sprites(folder_path, output_horizontal, output_vertical):
images = [Image.open(os.path.join(folder_path, f)) for f in os.listdir(folder_path) if f.endswith(('.png', '.jpg', '.jpeg'))]
if not images:
return None, None
width, height = images[0].size
# Horizontal merge
total_width = width * len(images)
horizontal_image = Image.new('RGBA', (total_width, height))
for i, img in enumerate(images):
horizontal_image.paste(img, (i * width, 0))
horizontal_image.save(output_horizontal, 'PNG')
# Vertical merge
total_height = height * len(images)
vertical_image = Image.new('RGBA', (width, total_height))
for i, img in enumerate(images):
vertical_image.paste(img, (0, i * height))
vertical_image.save(output_vertical, 'PNG')
return horizontal_image, vertical_image
class TestSpriteMerger(unittest.TestCase):
def setUp(self):
self.test_folder = 'test_images'
self.size = (50, 20)
os.makedirs(self.test_folder, exist_ok=True)
for i in range(3):
create_test_image(os.path.join(self.test_folder, f'test_{i+1}.png'), self.size, i+1)
def test_merge_horizontal(self):
output_h = 'test_merged_horizontal.png'
output_v = 'test_merged_vertical.png'
h_img, _ = merge_sprites(self.test_folder, output_h, output_v)
self.assertIsNotNone(h_img, "Horizontal merge failed")
self.assertEqual(h_img.size, (self.size[0] * 3, self.size[1]))
def test_merge_vertical(self):
output_h = 'test_merged_horizontal.png'
output_v = 'test_merged_vertical.png'
_, v_img = merge_sprites(self.test_folder, output_h, output_v)
self.assertIsNotNone(v_img, "Vertical merge failed")
self.assertEqual(v_img.size, (self.size[0], self.size[1] * 3))
def tearDown(self):
if os.path.exists(self.test_folder):
shutil.rmtree(self.test_folder)
for f in ['test_merged_horizontal.png', 'test_merged_vertical.png']:
if os.path.exists(f):
os.remove(f)
class SpriteMergerApp(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.setWindowTitle("Sprite Merger")
self.setGeometry(100, 100, 800, 600)
self.folder_path = ""
layout = QVBoxLayout()
self.select_button = QPushButton("Select Folder")
self.select_button.clicked.connect(self.select_folder)
layout.addWidget(self.select_button)
self.merge_type = QComboBox()
self.merge_type.addItems(["Horizontal", "Vertical"])
layout.addWidget(self.merge_type)
self.process_button = QPushButton("Process Selected Folder")
self.process_button.clicked.connect(self.process_folder)
layout.addWidget(self.process_button)
self.test_button = QPushButton("Run Unit Test")
self.test_button.clicked.connect(self.run_unit_test)
layout.addWidget(self.test_button)
self.result_label = QLabel("No image processed")
layout.addWidget(self.result_label)
self.image_label = QLabel()
layout.addWidget(self.image_label)
container = QWidget()
container.setLayout(layout)
self.setCentralWidget(container)
def select_folder(self):
self.folder_path = QFileDialog.getExistingDirectory(self, "Select Sprite Folder")
self.result_label.setText(f"Selected: {self.folder_path}")
def process_folder(self):
if not self.folder_path:
self.result_label.setText("Please select a folder first")
return
h_img, v_img = merge_sprites(self.folder_path, 'merged_horizontal.png', 'merged_vertical.png')
selected_type = self.merge_type.currentText()
img = h_img if selected_type == "Horizontal" else v_img
if img:
pixmap = QPixmap.fromImage(ImageQt.ImageQt(img))
self.image_label.setPixmap(pixmap.scaled(700, 500, aspectRatioMode=Qt.AspectRatioMode.KeepAspectRatio))
self.result_label.setText(f"{selected_type} merge completed")
else:
self.result_label.setText(f"{selected_type} merge failed")
def run_unit_test(self):
suite = unittest.TestLoader().loadTestsFromTestCase(TestSpriteMerger)
result = unittest.TextTestRunner().run(suite)
test_folder = 'test_images'
os.makedirs(test_folder, exist_ok=True)
for i in range(3):
create_test_image(os.path.join(test_folder, f'test_{i+1}.png'), (50, 20), i+1)
h_img, v_img = merge_sprites(test_folder, 'test_merged_horizontal.png', 'test_merged_vertical.png')
selected_type = self.merge_type.currentText()
img = h_img if selected_type == "Horizontal" else v_img
if img:
pixmap = QPixmap.fromImage(ImageQt.ImageQt(img))
self.image_label.setPixmap(pixmap.scaled(700, 500, aspectRatioMode=Qt.AspectRatioMode.KeepAspectRatio))
self.result_label.setText(f"Unit tests: {result.testsRun} run, {len(result.failures)} failed, showing {selected_type.lower()} merge")
else:
self.result_label.setText(f"Unit tests: {result.testsRun} run, {len(result.failures)} failed, merge failed")
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = SpriteMergerApp()
window.show()
sys.exit(app.exec())Wednesday, July 2, 2025
Python Qt6 : ... simple resize image files.
import sys
import os
from datetime import datetime
from PyQt6.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QWidget, QVBoxLayout, QPushButton, QFileDialog, QLineEdit, QCheckBox, QLabel, QMessageBox
from PyQt6.QtCore import Qt
from PIL import Image
class ResizeApp(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.setWindowTitle("Image Resizer")
self.setGeometry(100, 100, 400, 200)
layout = QVBoxLayout()
central_widget = QWidget()
central_widget.setLayout(layout)
self.setCentralWidget(central_widget)
self.folder_button = QPushButton("Select Folder")
self.folder_button.clicked.connect(self.select_folder)
layout.addWidget(self.folder_button)
self.width_edit = QLineEdit("800")
self.width_edit.setPlaceholderText("Width (px)")
layout.addWidget(QLabel("Width:"))
layout.addWidget(self.width_edit)
self.height_edit = QLineEdit("600")
self.height_edit.setPlaceholderText("Height (px)")
layout.addWidget(QLabel("Height:"))
layout.addWidget(self.height_edit)
self.aspect_ratio = QCheckBox("Maintain Aspect Ratio")
self.aspect_ratio.setChecked(True)
layout.addWidget(self.aspect_ratio)
self.resize_button = QPushButton("Resize Images")
self.resize_button.clicked.connect(self.resize_images)
layout.addWidget(self.resize_button)
self.folder_path = ""
def select_folder(self):
self.folder_path = QFileDialog.getExistingDirectory(self, "Select Image Folder")
if self.folder_path:
self.folder_button.setText(f"Selected: {os.path.basename(self.folder_path)}")
def resize_images(self):
if not self.folder_path:
QMessageBox.warning(self, "Error", "Please select a folder.")
return
try:
width = int(self.width_edit.text())
height = int(self.height_edit.text())
except ValueError:
QMessageBox.warning(self, "Error", "Please enter valid width and height.")
return
if width <= 0 or height <= 0:
QMessageBox.warning(self, "Error", "Width and height must be positive.")
return
date_str = datetime.now().strftime("%d%m%y_%H%M")
aspect_str = "asp_on" if self.aspect_ratio.isChecked() else "asp_off"
output_folder = os.path.join(self.folder_path, f"resized_{date_str}_{height}_{aspect_str}")
os.makedirs(output_folder, exist_ok=True)
for file_name in os.listdir(self.folder_path):
if file_name.lower().endswith(('.png', '.jpg', '.jpeg', '.bmp', '.gif')):
image_path = os.path.join(self.folder_path, file_name)
try:
with Image.open(image_path) as img:
if self.aspect_ratio.isChecked():
img.thumbnail((width, height), Image.Resampling.LANCZOS)
else:
img = img.resize((width, height), Image.Resampling.LANCZOS)
output_path = os.path.join(output_folder, f"resized_{date_str}_{height}_{aspect_str}_{file_name}")
img.save(output_path)
except Exception as e:
QMessageBox.warning(self, "Error", f"Failed to process {file_name}: {str(e)}")
QMessageBox.information(self, "Success", f"Images resized and saved to {output_folder}!")
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = ResizeApp()
window.show()
sys.exit(app.exec())Thursday, May 8, 2025
Python 3.11.11 : Colab simple image to video with stabilityai - part 052.
pipe = StableVideoDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
'stabilityai/stable-video-diffusion-img2vid-xt',
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
variant='fp16'
)
pipe.enable_model_cpu_offload()Saturday, February 8, 2025
Python 3.13.0rc1 : Testing python with Ollama local install.
import subprocess
import os
import json
from PIL import Image, ImageOps
class OllamaProcessor:
def __init__(self, config_file):
self.config_file = config_file
self.model_methods = self.load_config()
def load_config(self):
try:
with open(self.config_file, 'r') as file:
config = json.load(file)
print("Configuration loaded successfully.")
return config
except FileNotFoundError:
print(f"Configuration file {self.config_file} not found.")
raise
except json.JSONDecodeError:
print(f"Error decoding JSON from the configuration file {self.config_file}.")
raise
def check_ollama(self):
try:
result = subprocess.run(["ollama", "--version"], capture_output=True, text=True, check=True)
print("Ollama is installed. Version:", result.stdout)
except subprocess.CalledProcessError as e:
print("Ollama is not installed or not found in PATH. Ensure it's installed and accessible.")
raise
... python ollama_test_001.py
Configuration file ollama_config.json created successfully.
Configuration loaded successfully.
Ollama is installed. Version: ollama version is 0.5.7
Available models: ['NAME']
pulling manifest
pulling 170370233dd5... 100% ▕██████████████▏ 4.1 GB
pulling 72d6f08a42f6... 100% ▕██████████████▏ 624 MB
pulling 43070e2d4e53... 100% ▕██████████████▏ 11 KB
pulling c43332387573... 100% ▕██████████████▏ 67 B
pulling ed11eda7790d... 100% ▕██████████████▏ 30 B
pulling 7c658f9561e5... 100% ▕██████████████▏ 564 B
verifying sha256 digest
writing manifest
success
Model llava pulled successfully for method process_images_in_folder.Tuesday, January 7, 2025
Python 3.13.0rc1 : Simple convert all webp files from folder.
import os
import sys
from PIL import Image
def convert_webp_to_png(directory):
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(directory):
for file in files:
if file.endswith(".webp"):
webp_path = os.path.join(root, file)
png_path = os.path.splitext(webp_path)[0] + ".png"
with Image.open(webp_path) as img:
img.save(png_path, "PNG")
print(f"webp to png file: {webp_path} -> {png_path}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
if len(sys.argv) != 2:
print("How to use: python convert.py path_to_folder_with_webp_files")
sys.exit(1)
directory = sys.argv[1]
if not os.path.isdir(directory):
print(f"{directory} folder is not valid.")
sys.exit(1)
convert_webp_to_png(directory)
print("Finished !")Sunday, November 24, 2024
Python 3.13.0 : emoji symbols with PIL.
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont
import os
# Font size and image dimensions
font_size = 88
width = 640
height = 480
# Use Symbola.ttf from current directory
font_path = "Symbola.ttf"
# Create image
img = Image.new('RGB', (width, height), color='white')
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
# Get font
font = ImageFont.truetype(font_path, font_size)
# Emoji matrix
emoji_matrix = [
['😀', '😁', '😂', '🤣', '😃'],
['😄', '😅', '😆', '😇', '😈'],
['😉', '😊', '😋', '😌', '😍'],
['😎', '😏', '😐', '😑', '😒']
]
# Calculate spacing
x_spacing = font_size + 10
y_spacing = font_size + 10
# Calculate starting position to center the grid
start_x = (width - (len(emoji_matrix[0]) * x_spacing)) // 2
start_y = (height - (len(emoji_matrix) * y_spacing)) // 2
# Draw emojis
for i, row in enumerate(emoji_matrix):
for j, emoji in enumerate(row):
x = start_x + (j * x_spacing)
y = start_y + (i * y_spacing)
draw.text((x, y), emoji, font=font, fill='black')
# Save the image
img.save('emoji_art.png')
print("Emoji art has been created successfully! Check emoji_art.png")

Tuesday, March 26, 2024
Python 3.12.1 : Read EXIF data with PIL.
import sys
import PIL
import PIL.Image as PILimage
from PIL import ImageDraw, ImageFont, ImageEnhance
from PIL.ExifTags import TAGS, GPSTAGS
class EXIF(object):
def __init__(self, img):
self.img = img
self.exif_data = self.get_exif_data()
self.lat = self.get_lat()
self.lon = self.get_lon()
self.date =self.get_date_time()
super(Worker, self).__init__()
@staticmethod
def get_if_exist(data, key):
if key in data:
return data[key]
return None
def get_exif_data(self):
"""Returns a dictionary from the exif data of an PIL Image item. Also
converts the GPS Tags"""
exif_data = {}
info = self.img._getexif()
if info:
for tag, value in info.items():
decoded = TAGS.get(tag, tag)
if decoded == "GPSInfo":
gps_data = {}
for t in value:
sub_decoded = GPSTAGS.get(t, t)
gps_data[sub_decoded] = value[t]
exif_data[decoded] = gps_data
else:
exif_data[decoded] = value
print('exif_data ===')
print(exif_data)
print('exif_data ===')
return exif_data
if __name__ == '__main__':
try:
img = PILimage.open(sys.argv[1])
image = EXIF(img)
except Exception as e:
print(e)python detect_exif_data_001.py paint.jpg
exif_data ===
{'ResolutionUnit': 2, 'ExifOffset': 196, 'Make': 'Canon', 'Model': '', 'Orientation': 1,
'DateTime': '2012:08:19 13:20:09', 'YCbCrPositioning': 1, 'XResolution': 180.0, 'YResolution': 180.0,
'ExifVersion': b'0220', 'ComponentsConfiguration': b'\x01\x02\x03\x00', 'CompressedBitsPerPixel': 5.0,
'DateTimeOriginal': '2012:08:19 13:20:09', 'DateTimeDigitized': '2012:08:19 13:20:09', 'ShutterSpeedValue': 4.3125,
'ApertureValue': 2.75, 'ExposureBiasValue': 0.0, 'MaxApertureValue': 2.75, 'MeteringMode': 5, 'Flash': 16,
'FocalLength': 5.8, 'UserComment':
...
'ColorSpace': 1, 'ExifImageWidth': 3072, 'FocalPlaneXResolution': 13653.333333333334, 'ExifImageHeight': 1728,
'FocalPlaneYResolution': 10224.852071005917, 'FocalPlaneResolutionUnit': 2, 'SensingMethod': 2, 'FileSource': b'\x03',
'ExposureTime': 0.05, 'ExifInteroperabilityOffset': 3334, 'FNumber': 2.6, 'CustomRendered': 0, 'ISOSpeedRatings': 80,
'ExposureMode': 0, 'FlashPixVersion': b'0100', 'WhiteBalance': 0, 'DigitalZoomRatio': 1.0, 'SceneCaptureType': 1,
'MakerNote' ...Monday, January 8, 2024
Python 3.12.1 : Create a simple color palette.

from PIL import Image, ImageDraw
# 640x640 pixeli with 10x10 squares 64x64
img = Image.new('RGB', (640, 640))
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
# color list
colors = []
# for 100 colors you need to set steps with 62,62,64
# or you can change 64,62,62 some little changes
for r in range(0, 256, 62):
for g in range(0, 256, 62):
for b in range(0, 256, 64):
colors.append((r, g, b))
# show result of colors and size up 100 items
print(colors)
print(len(colors))
# create 10x10 colors and fill the image
for i in range(10):
for j in range(10):
x0 = j * 64
y0 = i * 64
x1 = x0 + 64
y1 = y0 + 64
color = colors[i*10 + j] # Selectarea culorii din lista
draw.rectangle([x0, y0, x1, y1], fill=color)
# save teh image
img.save('rgb_color_matrix.png')Monday, July 24, 2017
Fix Gimp with python script.
From my point of view, Gimp does not properly import frames from GIF files.
This program imports GIF files in this way:
Using the python module, you can get the correct frames from the GIF file.
Here's my script that uses the python PIL module.
import sys
from PIL import Image, ImageSequence
try:
img = Image.open(sys.argv[1])
except IOError:
print "Cant load", infile
sys.exit(1)
pal = img.getpalette()
prev = img.convert('RGBA')
prev_dispose = True
for i, frame in enumerate(ImageSequence.Iterator(img)):
dispose = frame.dispose
if frame.tile:
x0, y0, x1, y1 = frame.tile[0][1]
if not frame.palette.dirty:
frame.putpalette(pal)
frame = frame.crop((x0, y0, x1, y1))
bbox = (x0, y0, x1, y1)
else:
bbox = None
if dispose is None:
prev.paste(frame, bbox, frame.convert('RGBA'))
prev.save('result_%03d.png' % i)
prev_dispose = False
else:
if prev_dispose:
prev = Image.new('RGBA', img.size, (0, 0, 0, 0))
out = prev.copy()
out.paste(frame, bbox, frame.convert('RGBA'))
out.save('result_%03d.png' % i)C:\Python27>python.exe convert_gif.py 0001.gif
Thursday, February 16, 2017
Compare two images: the histogram method.
The example come with alternative solution: Histogram method.
The script was run under Fedora 25.
If the images are the same the result will be 0.0.
For testing I change the image2.png by make a line into this with a coverage of 10%.
The result of the script was:
1116.63243729
The images come with this dimensions: 738 x 502 px.
import math
import operator
from math import *
import PIL
from PIL import Image
h1 = Image.open("image1.png").histogram()
h2 = Image.open("image2.png").histogram()
rms = math.sqrt(reduce(operator.add,
map(lambda a,b: (a-b)**2, h1, h2))/len(h1))
print rms
Example:
operator.lt(a, b)
operator.le(a, b)
operator.eq(a, b)
operator.ne(a, b)
operator.ge(a, b)
operator.gt(a, b)
operator.__lt__(a, b)
operator.__le__(a, b)
operator.__eq__(a, b)
operator.__ne__(a, b)
operator.__ge__(a, b)
operator.__gt__(a, b)This is like math operators:
lt(a, b) is equivalent to a < b
le(a, b) is equivalent to a <= b
Another example:
>>> # Elementwise multiplication
>>> map(mul, [0, 1, 2, 3], [10, 20, 30, 40])
[0, 20, 60, 120]
>>> # Dot product
>>> sum(map(mul, [0, 1, 2, 3], [10, 20, 30, 40]))
200
Thursday, August 11, 2016
Hide your info with stepic python module.
First you need one image. I used this image:
First need to use Python 2.7 with Image ( Pillow python module) and stepic python module.
... and follow the below steps:
C:\Python27>cd Scripts
C:\Python27\Scripts>pip install Image
C:\Python27\Scripts>pip install stepic
C:\Python27\Scripts>cd ..
C:\Python27>python
Python 2.7.8 (default, Jun 30 2014, 16:08:48) [MSC v.1500 64 bit (AMD64)] on win32
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
To encode and then to show the text from one image I used this python script:
import PIL
from PIL import Image
import stepic
im=Image.open("MonaLisa.jpg")
im1 = stepic.encode(im,'The smallest feline is a masterpiece.')
im1.save('test_encode.jpg','JPEG')
im.show()
im1.show()
decoding=stepic.decode(im1)
data_encode=decoding.decode()
print data_encode
Sunday, August 23, 2015
Pillow python module with Python 3.4.1 .
I used pip3.4 and python 3.4.1 version.
Some problems about how to write your source code can be found : porting pil to pillow.
Thursday, October 17, 2013
How to make a color gradient and images with python script.
The Image and ImageDraw provide simple 2D graphics to create new images, annotate or retouch existing images, and to generate graphics.
Also this can help you to make on the fly images for you.
Let's see one example ...
First you need to import this modules and random python module
import Image,ImageDraw
from random import randint as rint The next step : make one image , get some random numbers...
You need two colors : first is one random color and second is make from first color, see next source code:
img = Image.new("RGB", (500,500), "#FFFFFF")
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
r,g,b = rint(0,255), rint(0,255), rint(0,255)
dr = (rint(0,255) - r)/500.
dg = (rint(0,255) - g)/500.
db = (rint(0,255) - b)/500. Now you need to draw lines with this gradient of two colors.
for i in range(500):
r,g,b = r+dr, g+dg, b+db
draw.line((i,0,i,500), fill=(int(r),int(g),int(b))) ... and the python script source code:
import Image,ImageDraw
from random import randint as rint
def random_gradient(name):
img = Image.new("RGB", (500,500), "#FFFFFF")
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
r,g,b = rint(0,255), rint(0,255), rint(0,255)
dr = (rint(0,255) - r)/500.
dg = (rint(0,255) - g)/500.
db = (rint(0,255) - b)/500.
for i in range(500):
r,g,b = r+dr, g+dg, b+db
draw.line((i,0,i,500), fill=(int(r),int(g),int(b)))
img.save(name+".png", "PNG")
if __name__ == "__main__":
for name in range(10):
random_gradient(str(name)) The result of this script will make images :

Monday, February 25, 2013
Make Newton fractal with python
A fractal is a mathematical set that has a fractal dimension that usually exceeds its topological dimension , see Fractal wikipedia.
Today I used my mind and also my python skills to make one fractal image.
I use Newton's method to make all points and PIL python module to save the result.
Let's see the source code and comments.
from PIL import Image
#size of image
imgx = 600
imgy = 400
#make image buffer
image = Image.new("RGB", (imgx, imgy))
# area of fractal
xa = -2.0
xb = 2.0
ya = -2.0
yb = 2.0
#define constants
max_iterations = 10 # max iterations allowed
step_derivat = 0.002e-1 # step size for numerical derivative
error = 5e-19 # max error allowed
# function will generate the newton fractal
def f(z): return z * z + complex(-0.31,0.031)
# draw derivate fractal for each y and x
for y in range(imgy):
zy = y * (yb - ya)/(imgy - 1) + ya
for x in range(imgx):
zx = x * (xb - xa)/(imgx - 1) + xa
z = complex(zx, zy)
for i in range(max_iterations):
# make complex numerical derivative
dz = (f(z + complex(step_derivat, step_derivat)) - f(z))/complex(step_derivat,step_derivat)
# Newton iteration see wikipedia
z0 = z - f(z)/dz
# stop to the error
if abs(z0 - z) < error:
break
z = z0
#I use modulo operation expression to do RGB colors of the pixels
image.putpixel((x, y), (i % 8 * 16, i % 4 * 32,i % 2 * 64))
#save the result
image.save("fractal.png", "PNG") This is the final result of Newton fractal image:

Sunday, December 16, 2012
Simple way to create png image with an input text.
First you need to have the PIL python module and import this.
from PIL import Image
from PIL import ImageDraw
from PIL import ImageFont
from PIL import ImageFilter Next will be this function.Basically will make and return one RGBA image data type.
def make_img(image, textColor, backgroundColor):
img = image.convert("RGBA")
img.putdata([textColor if value == 0 else backgroundColor
for value in image.getdata()])
return img The next step is to set the text , font and the new image.
I use Arggotsc.ttf. You can use any TrueType font.
text = " Inca un script in python! "
font = ImageFont.truetype('Arggotsc.ttf', 55)
image = Image.new("1", font.getsize(text), '#FFF') Now we can draw, add text, resize, bur the text and finally save the image.
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(image)
draw.text((0, 0), text, font=font)
image = image.resize([i for i in image.size], Image.NEAREST)
imgText = make_img(image, (200, 200, 200), (0, 0, 0, 0))
blur_img = make_img(image, (0, 0, 0), (0, 0, 0, 0))
for i in range(3):
blur_img = blur_img.filter(ImageFilter.BLUR)
blur_img.paste(imgText, (0, 0), imgText)
blur_img.save("text-img.png") The result is:
See you later with another tutorial.
Thursday, September 13, 2012
Simple python script - Voronoi diagram
Today I show you how to make Voronoi diagram using python.
I use this to make textures for underwater.
This is just one example. But you can improve to control all cells of voronoi diagram.
The theory say:
In mathematics, a Voronoi diagram is a special kind of decomposition of a metric space, determined by distances to a specified family of objects (subsets) in the space. These objects are usually called the sites or the generators...Source : wikipedia.
I used the euclidean distance to make the Voronoi diagram because it's the most familiar case.
About wikipedia - Euclidean_distance: In mathematics, the Euclidean distance or Euclidean metric is the "ordinary" distance between two points that one would measure with a ruler, and is given by the Pythagorean formula...
My python script use the next python modules:
PIL - this allow me to use image functions.
random - this module give me... random numbers.
math - some math functions.
Let's see the source code :
from PIL import Image
import random
import math
Now I make the function named gen_voronoi.
This take the height and width of the output image and the number of cells.
The function has some random variables for red , green , blue - nr,ng,nb.
The function hypot is not accessible directly so we need to import math module and using math static object.
The return value is the Euclidean norm : sqrt(x*x + y*y).
def gen_voronoi(w, h, cells):
image = Image.new("RGB", (w, h))
putpixel = image.putpixel
img_x, img_y = image.size
nx = []
ny = []
nr = []
ng = []
nb = []
for i in range(cells):
nx.append(random.randrange(img_x))
ny.append(random.randrange(img_y))
nr.append(random.randrange(256))
ng.append(random.randrange(256))
nb.append(random.randrange(256))
for y in range(img_y):
for x in range(img_x):
dmin = math.hypot(img_x-1, img_y-1)
j = -1
for i in range(cells):
d = math.hypot(nx[i]-x, ny[i]-y)
if d < dmin:
dmin = d
j = i
putpixel((x, y), (nr[j], ng[j], nb[j]))
image.save("output.png", "PNG")
image.show()
Use the function to make the output.png image.
gen_voronoi(200, 200, 55)
The result is :

Monday, April 30, 2012
Create tile image for your game using python script
Tile image is a method of storing a sequence of images placed in a single image file.
These images are then processed according to user needs.
Here's an example below:
How we can create these images?
We can use graphics editing software to create them separately.
I used Blender 3D to create separate images.
A tutorial how to do this can be found here on section Blender 3D.
After I rendered images separately and named: 0000.png , 0001.png , 0002.png , 0003.png
I created a python script to put in an tile image, see below:
import os
import PIL
from PIL import Image
from PIL import ImageDraw
o=Image.new("RGBA",(192,48))
d= ImageDraw.Draw(o)
for pic in range(0,4):
strpic=str(pic)
filnam="000"+strpic+".png"
x=pic*48
img=Image.open(filnam)
o.paste(img,(0+x,0))
o.save("out.png")Resize screenshot with PIL python module .
"""
This python script read the name of image and will create a new image with the given width and height.
$ python imgresz.py
filename input image:test.png
test.png
filename output image:test-out.jpg
->width:500
->height:400
"""
import os
import sys
from PIL import Image
from PIL import ImageDraw
filnaminp=raw_input("filename input image:")
filnamout=raw_input("filename output image:")
w=input("->width:")
h=input("->height:")
imgi=Image.open(str(filnaminp))
imgo=imgi.resize((w,h),Image.BILINEAR)
imgo.save(str(filnamout))Sunday, June 27, 2010
Add text on image with PIL module.
This is the script:
import PIL
from PIL import ImageFont
from PIL import Image
from PIL import ImageDraw
font = ImageFont.truetype("/usr/share/fonts/dejavu/DejaVuSans.ttf",25)
img=Image.new("RGBA", (200,200),(120,20,20))
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
draw.text((0, 0),"This is a test",(255,255,0),font=font)
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
img.save("a_test.png")
The only error that can occur is not to find the font.In this case you must change the code line:
font = ImageFont.truetype("/usr/share/fonts/dejavu/DejaVuSans.ttf",25)
Here is the result script:
