Today I installed it again with all of these python packages using the pip tool.
You don't need all of these if you just start, but in time you will need to install them:
pip install sunpy --user
Collecting sunpy
Downloading sunpy-4.1.3.tar.gz (3.6 MB)
---------------------------------------- 3.6/3.6 MB 3.6 MB/s eta 0:00:00
...
Successfully installed PyYAML-6.0 aioftp-0.21.4 astropy-5.2.1 pyerfa-2.0.0.1 sunpy-4.1.3
...
pip install zeep --user
Collecting zeep
Using cached zeep-4.2.1-py3-none-any.whl (101 kB)
...
Successfully installed isodate-0.6.1 pytz-2022.7.1 requests-file-1.5.1 requests-toolbelt-0.10.1 zeep-4.2.1
...
pip install drms --user
Collecting drms
Downloading drms-0.6.3-py3-none-any.whl (35 kB)
...
Successfully installed drms-0.6.3 pandas-1.5.3
pip install hvpy --user
Collecting hvpy
Downloading hvpy-1.0.1-py3-none-any.whl (44 kB)
---------------------------------------- 44.0/44.0 kB 359.5 kB/s eta 0:00:00
...
Successfully installed hvpy-1.0.1
pip install scipy --user
Collecting scipy
Downloading scipy-1.10.1-cp311-cp311-win_amd64.whl (42.2 MB)
---------------------------------------- 42.2/42.2 MB 7.4 MB/s eta 0:00:00
...
Successfully installed scipy-1.10.1
pip install glymur --user
Collecting glymur
Downloading Glymur-0.12.2-py3-none-any.whl (2.7 MB)
---------------------------------------- 2.7/2.7 MB 4.2 MB/s eta 0:00:00
...
Successfully installed glymur-0.12.2
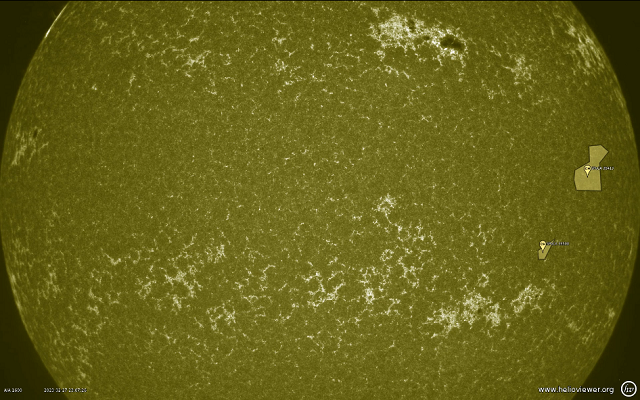
Let's use the 1600 Angstrom from these all data of spectral range: 335 Angstrom, 131 Angstrom, 191-195 Angstrom, 211 Angstrom, 1600 Angstrom, 1700 Angstrom, 4500 Angstrom, 171-175 Angstrom, 304 Angstrom, 94 Angstrom
from datetime import datetime
from hvpy import createMovie, DataSource, create_events, create_layers
createMovie(
startTime=datetime(2023, 2, 27), # start from 1st September 2022
endTime=datetime(2023, 2, 28), # end at 5th September 2022
layers=create_layers([(DataSource.AIA_1600, 100)]), # use AIA_193 Lens with 100% Opacity
events=create_events(["CH"]), # show the Active regions
eventsLabels=True, # event labels should be included
imageScale=1, # Image scale in arcseconds per pixel
hq=True, # Download a higher-quality movie file
timeout=10, # Wait 10 minutes to get a response
overwrite=True
)
The result is a video that looks like this :
There are easier ways to get information about the sun…
https://api.helioviewer.org/v2/takeScreenshot/?imageScale=1&layers=[SDO,AIA,AIA,304,1,100]&events=&eventLabels=true&scale=true&scaleType=earth&scaleX=0&scaleY=0&date=2023-02-28T15:00:00.000Z&x1=-1100.0&x2=1100.0&y1=-1100.0&y2=1100.0&display=true&watermark=true&events=[CH,all,1]