Two notebook on my colab repo project
One with xterm colab festure and another with hull-convex known as lattrice with OllamaFunctions.
Is a blog about python programming language. You can see my work with python programming language, tutorials and news.


bl_info = {
"name": "3D File Renderer by catafest",
"blender": (4, 3, 2),
"category": "Object",
"author": "Catalin George Festila\n"
"nicknames: catafest and mythcat\n"
"country: Romania\n"
"mail: catafest [at] yahoo.com",
"version": (1, 0),
"blender": (2, 80, 0),
"location": "View3D > UI > 3D File Renderer",
"description": "Addon for rendering 3D files",
"warning": "",
"doc_url": "https://github.com/catafest",
"tracker_url": "https://github.com/catafest/issues",
"support": "COMMUNITY",
}
import bpy
import os
class FileRendererProperties(bpy.types.PropertyGroup):
input_directory: bpy.props.StringProperty(
name="Input Directory",
description="Directory containing 3D files",
default="",
maxlen=1024,
subtype='DIR_PATH'
)
output_directory: bpy.props.StringProperty(
name="Output Directory",
description="Directory to save rendered images",
default="",
maxlen=1024,
subtype='DIR_PATH'
)
class RENDER_OT_files(bpy.types.Operator):
bl_idname = "render.files"
bl_label = "Start render 3D files for all files"
def execute(self, context):
input_directory = context.scene.file_renderer_props.input_directory
output_directory = context.scene.file_renderer_props.output_directory
if not input_directory or not output_directory:
self.report({'ERROR'}, "Input and Output directories must be set.")
return {'CANCELLED'}
if not os.path.exists(output_directory):
os.makedirs(output_directory)
def render_file(file_path, output_path):
try:
bpy.ops.wm.read_factory_settings(use_empty=True)
ext = os.path.splitext(file_path)[1].lower()
if ext == ".glb":
bpy.ops.import_scene.gltf(filepath=file_path)
elif ext == ".obj":
bpy.ops.import_scene.obj(filepath=file_path)
elif ext == ".fbx":
bpy.ops.import_scene.fbx(filepath=file_path)
else:
raise ValueError("Unsupported file format")
bpy.ops.object.camera_add(location=(0, -3, 1.5), rotation=(1.1, 0, 0))
camera = bpy.context.scene.objects['Camera']
bpy.context.scene.camera = camera
bpy.ops.object.light_add(type='POINT', location=(0, -3, 3))
light = bpy.context.view_layer.objects.active
light.data.energy = 1000
bpy.context.scene.render.resolution_x = 512
bpy.context.scene.render.resolution_y = 512
bpy.context.scene.render.filepath = output_path
bpy.ops.render.render(write_still=True)
except Exception as e:
# Generate a red image with "BAD FILE" text using Blender
bpy.ops.wm.read_factory_settings(use_empty=True)
bpy.ops.mesh.primitive_plane_add(size=2)
plane = bpy.context.active_object
mat = bpy.data.materials.new(name="BadFileMaterial")
mat.diffuse_color = (1, 0, 0, 1) # Red
plane.data.materials.append(mat)
# Add "BAD FILE" text
bpy.ops.object.text_add(location=(0, 0, 0.1))
text_obj = bpy.context.active_object
text_obj.data.body = "BAD FILE"
text_obj.data.size = 0.5
text_obj.data.align_x = 'CENTER'
text_obj.data.align_y = 'CENTER'
text_obj.rotation_euler = (1.5708, 0, 0)
# Set camera and light
bpy.ops.object.camera_add(location=(0, -3, 1.5), rotation=(1.1, 0, 0))
camera = bpy.context.scene.objects['Camera']
bpy.context.scene.camera = camera
bpy.ops.object.light_add(type='POINT', location=(0, -3, 3))
light = bpy.context.view_layer.objects.active
light.data.energy = 1000
bpy.context.scene.render.resolution_x = 512
bpy.context.scene.render.resolution_y = 512
bpy.context.scene.render.filepath = output_path
bpy.ops.render.render(write_still=True)
for filename in os.listdir(input_directory):
if filename.lower().endswith((".glb", ".obj", ".fbx")):
file_path = os.path.join(input_directory, filename)
output_path = os.path.join(output_directory, os.path.splitext(filename)[0] + ".png")
render_file(file_path, output_path)
self.report({'INFO'}, "Rendering of files is complete.")
return {'FINISHED'}
class ABOUT_OT_dialog(bpy.types.Operator):
bl_idname = "wm.about_dialog"
bl_label = "About this addon"
def execute(self, context):
return context.window_manager.invoke_props_dialog(self)
def draw(self, context):
layout = self.layout
layout.label(text="3D File Renderer by catafest")
layout.label(text="Author: Catalin George Festila")
layout.label(text="Nicknames: catafest and mythcat")
layout.label(text="Country: Romania")
layout.label(text="Email: catafest [at] yahoo.com")
layout.operator("wm.url_open", text="LinkedIn").url = "https://www.linkedin.com/in/c%C4%83t%C4%83lin-george-fe%C8%99til%C4%83-05780a67"
layout.operator("wm.url_open", text="Author Site").url = "https://sites.google.com/view/festila-george-catalin"
layout.operator("wm.url_open", text="catafest GitHub").url = "https://github.com/catafest"
layout.operator("wm.url_open", text="catafest-work GitHub").url = "https://github.com/catafest-work"
class FileRendererPanel(bpy.types.Panel):
bl_label = "3D File Renderer by catafest"
bl_idname = "OBJECT_PT_file_renderer"
bl_space_type = 'VIEW_3D'
bl_region_type = 'UI'
bl_category = 'File Renderer'
def draw(self, context):
layout = self.layout
scene = context.scene
file_renderer_props = scene.file_renderer_props
layout.prop(file_renderer_props, "input_directory")
layout.prop(file_renderer_props, "output_directory")
# Styling the render button
render_button = layout.operator("render.files", text="Start render 3D files for all files")
layout.separator()
layout.operator("wm.about_dialog", text="About this addon")
def register():
bpy.utils.register_class(FileRendererProperties)
bpy.utils.register_class(RENDER_OT_files)
bpy.utils.register_class(ABOUT_OT_dialog)
bpy.utils.register_class(FileRendererPanel)
bpy.types.Scene.file_renderer_props = bpy.props.PointerProperty(type=FileRendererProperties)
def unregister():
bpy.utils.unregister_class(FileRendererProperties)
bpy.utils.unregister_class(RENDER_OT_files)
bpy.utils.unregister_class(ABOUT_OT_dialog)
bpy.utils.unregister_class(FileRendererPanel)
del bpy.types.Scene.file_renderer_props
if __name__ == "__main__":
register()

import bpy, bmesh
obj = bpy.context.active_object
me = obj.data
bpy.ops.object.mode_set(mode = 'EDIT')
bpy.ops.mesh.select_mode(type="VERT")
bm = bmesh.from_edit_mesh(obj.data)
selected = [False,False,True,True,True,True,True,True]
verts = [vert for vert in bpy.context.active_object.data.vertices if vert.select]
all = [vert for vert in bpy.context.active_object.data.vertices]
print("selected:",len(verts))
print("all:",len(all))
bpy.ops.object.mode_set(mode = 'OBJECT')
me.vertices.foreach_set(
"select",
selected
)
bpy.ops.object.mode_set(mode = 'EDIT')
# give Python access to Blender's functionality
import bpy
# extend Python's math functionality
import math
# extend Python functionality to generate random numbers
import random
def partially_clean_the_scene():
# select all object in the scene
bpy.ops.object.select_all(action="SELECT")
# delete all selected objects in the scene
bpy.ops.object.delete()
# make sure we remove data that was connected to the objects we just deleted
bpy.ops.outliner.orphans_purge(do_local_ids=True, do_linked_ids=True, do_recursive=True)
def create_noise_mask(material):
"""Add a set of nodes to create a noise mask using:
* Texture Coordinate node
* Mapping node
* Noise Texture node
* Color Ramp node
"""
node_location_x_step = 300
node_location_x = -node_location_x_step
# create a Color Ramp node
# https://docs.blender.org/api/current/bpy.types.ShaderNodeValToRGB.html
color_ramp_node = material.node_tree.nodes.new(type="ShaderNodeValToRGB")
color_ramp_node.color_ramp.elements[0].position = 0.45
color_ramp_node.color_ramp.elements[1].position = 0.5
color_ramp_node.location.x = node_location_x
node_location_x -= node_location_x_step
# create a Noise Texture node
# https://docs.blender.org/api/current/bpy.types.ShaderNodeTexNoise.html#bpy.types.ShaderNodeTexNoise
noise_texture_node = material.node_tree.nodes.new(type="ShaderNodeTexNoise")
noise_texture_node.inputs["Scale"].default_value = random.uniform(1.0, 20.0)
noise_texture_node.location.x = node_location_x
node_location_x -= node_location_x_step
# create a Mapping node
# https://docs.blender.org/api/current/bpy.types.ShaderNodeMapping.html#bpy.types.ShaderNodeMapping
mapping_node = material.node_tree.nodes.new(type="ShaderNodeMapping")
mapping_node.inputs["Rotation"].default_value.x = math.radians(random.uniform(0.0, 360.0))
mapping_node.inputs["Rotation"].default_value.y = math.radians(random.uniform(0.0, 360.0))
mapping_node.inputs["Rotation"].default_value.z = math.radians(random.uniform(0.0, 360.0))
mapping_node.location.x = node_location_x
node_location_x -= node_location_x_step
# create a Texture Coordinate node
texture_coordinate_node = material.node_tree.nodes.new(type="ShaderNodeTexCoord")
texture_coordinate_node.location.x = node_location_x
# connect the nodes
# https://docs.blender.org/api/current/bpy.types.NodeTree.html#bpy.types.NodeTree
# https://docs.blender.org/api/current/bpy.types.NodeLinks.html#bpy.types.NodeLinks
material.node_tree.links.new(noise_texture_node.outputs["Color"], color_ramp_node.inputs["Fac"])
material.node_tree.links.new(mapping_node.outputs["Vector"], noise_texture_node.inputs["Vector"])
material.node_tree.links.new(texture_coordinate_node.outputs["Generated"], mapping_node.inputs["Vector"])
return color_ramp_node
def create_material(name):
# create new material
material = bpy.data.materials.new(name=name)
# enable creating a material via nodes
material.use_nodes = True
# get a reference to the Principled BSDF shader node
principled_bsdf_node = material.node_tree.nodes["Principled BSDF"]
# set the base color of the material
principled_bsdf_node.inputs["Base Color"].default_value = (0.8, 0.120827, 0.0074976, 1)
# set the metallic value of the material
principled_bsdf_node.inputs["Metallic"].default_value = 1.0
color_ramp_node = create_noise_mask(material)
material.node_tree.links.new(color_ramp_node.outputs["Color"], principled_bsdf_node.inputs["Roughness"])
return material
def add_mesh():
# create an ico sphere
bpy.ops.mesh.primitive_ico_sphere_add(subdivisions=5)
# shade smooth
bpy.ops.object.shade_smooth()
# get reference to mesh object
mesh_obj = bpy.context.active_object
return mesh_obj
def main():
partially_clean_the_scene()
name = "my_generated_material"
material = create_material(name)
mesh_obj = add_mesh()
# apply the material to the mesh object
mesh_obj.data.materials.append(material)
main()
import gradio as gr
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
import torch
model_id = "dream-textures/texture-diffusion"
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(model_id, torch_dtype=torch.float16)
pipe = pipe.to("cuda")
def generate_image(prompt):
image = pipe(prompt).images[0]
image.save("result.png")
return image
iface = gr.Interface(
fn=generate_image,
inputs="text",
outputs="image",
title="Stable Diffusion Image Generator",
description="Introduceți un prompt pentru a genera o imagine folosind Stable Diffusion."
)
iface.launch()
import os
import sys
from PIL import Image
def convert_webp_to_png(directory):
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(directory):
for file in files:
if file.endswith(".webp"):
webp_path = os.path.join(root, file)
png_path = os.path.splitext(webp_path)[0] + ".png"
with Image.open(webp_path) as img:
img.save(png_path, "PNG")
print(f"webp to png file: {webp_path} -> {png_path}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
if len(sys.argv) != 2:
print("How to use: python convert.py path_to_folder_with_webp_files")
sys.exit(1)
directory = sys.argv[1]
if not os.path.isdir(directory):
print(f"{directory} folder is not valid.")
sys.exit(1)
convert_webp_to_png(directory)
print("Finished !")mythcat@fedora:~$ pip install unstructured
Defaulting to user installation because normal site-packages is not writeable
Collecting unstructured
Downloading unstructured-0.11.8-py3-none-any.whl.metadata (26 kB)
...
Successfully installed aiofiles-24.1.0 annotated-types-0.7.0 anyio-4.7.0 backoff-2.2.1 beautifulsoup4-4.12.3 chardet-5.2.0 click-8.1.8 cryptography-44.0.0 dataclasses-json-0.6.7 emoji-2.14.0 eval-type-backport-0.2.2 filetype-1.2.0 h11-0.14.0 httpcore-1.0.7 httpx-0.28.1 jsonpath-python-1.0.6 langdetect-1.0.9 marshmallow-3.23.2 mypy-extensions-1.0.0 nest-asyncio-1.6.0 nltk-3.9.1 pydantic-2.9.2 pydantic-core-2.23.4 pypdf-5.1.0 python-iso639-2024.10.22 python-magic-0.4.27 rapidfuzz-3.11.0 requests-toolbelt-1.0.0 sniffio-1.3.1 soupsieve-2.6 tabulate-0.9.0 tqdm-4.67.1 typing-extensions-4.12.2 typing-inspect-0.9.0 unstructured-0.11.8 unstructured-client-0.28.1 wrapt-1.17.0pip install unstructured-inference
Collecting unstructured-inference
...
note: This error originates from a subprocess, and is likely not a problem with pip.
ERROR: Failed building wheel for onnx
Failed to build onnx
ERROR: ERROR: Failed to build installable wheels for some pyproject.toml based projects (onnx)
mythcat@fedora:~$ pip install unstructured[pdf]
...
note: This error originates from a subprocess, and is likely not a problem with pip.
ERROR: Failed building wheel for onnx
Failed to build onnx
ERROR: ERROR: Failed to build installable wheels for some pyproject.toml based projects (onnx)Python 3.12.8 (main, Dec 6 2024, 00:00:00) [GCC 14.2.1 20240912 (Red Hat 14.2.1-3)] on linuxmythcat@localhost:~$ python3.12 -m pip install quil --usermythcat@localhost:~$ curl https://bootstrap.pypa.io/get-pip.py | python3.12 -
...
Installing collected packages: pip
Successfully installed pip-24.3.1mythcat@localhost:~$ python3.12 -m pip install quil --user
Collecting quilroot@localhost:/home/mythcat# dnf5 install python3-opencv.x86_64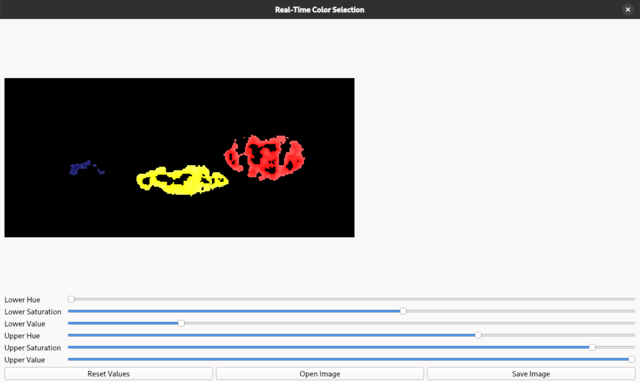
import sys
import cv2
import numpy as np
from PyQt6.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QWidget, QVBoxLayout, QLabel, QSlider, QFileDialog, QPushButton, QHBoxLayout
from PyQt6.QtGui import QImage, QPixmap
from PyQt6.QtCore import Qt, pyqtSlot
class MainWindow(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.setWindowTitle("Real-Time Color Selection")
self.setGeometry(100, 100, 1200, 800)
# Create central widget and main layout
central_widget = QWidget()
self.setCentralWidget(central_widget)
main_layout = QVBoxLayout(central_widget)
# Create image label
self.image_label = QLabel()
main_layout.addWidget(self.image_label)
# Initialize sliders
self.lower_h = QSlider(Qt.Orientation.Horizontal)
self.lower_s = QSlider(Qt.Orientation.Horizontal)
self.lower_v = QSlider(Qt.Orientation.Horizontal)
self.upper_h = QSlider(Qt.Orientation.Horizontal)
self.upper_s = QSlider(Qt.Orientation.Horizontal)
self.upper_v = QSlider(Qt.Orientation.Horizontal)
# Set slider ranges
for slider in [self.lower_h, self.upper_h]:
slider.setRange(0, 179)
for slider in [self.lower_s, self.lower_v, self.upper_s, self.upper_v]:
slider.setRange(0, 255)
# Set initial slider values
self.lower_h.setValue(50)
self.lower_s.setValue(100)
self.lower_v.setValue(50)
self.upper_h.setValue(130)
self.upper_s.setValue(255)
self.upper_v.setValue(255)
# Connect sliders to update function
self.lower_h.valueChanged.connect(self.update_hsv_range)
self.lower_s.valueChanged.connect(self.update_hsv_range)
self.lower_v.valueChanged.connect(self.update_hsv_range)
self.upper_h.valueChanged.connect(self.update_hsv_range)
self.upper_s.valueChanged.connect(self.update_hsv_range)
self.upper_v.valueChanged.connect(self.update_hsv_range)
# Create slider layouts with labels
sliders_layout = QVBoxLayout()
# Add slider pairs with labels
slider_pairs = [
("Lower Hue", self.lower_h),
("Lower Saturation", self.lower_s),
("Lower Value", self.lower_v),
("Upper Hue", self.upper_h),
("Upper Saturation", self.upper_s),
("Upper Value", self.upper_v)
]
for label_text, slider in slider_pairs:
row_layout = QHBoxLayout()
label = QLabel(label_text)
label.setMinimumWidth(120)
row_layout.addWidget(label)
row_layout.addWidget(slider)
sliders_layout.addLayout(row_layout)
main_layout.addLayout(sliders_layout)
# Add buttons
button_layout = QHBoxLayout()
self.reset_button = QPushButton("Reset Values")
self.reset_button.clicked.connect(self.reset_values)
button_layout.addWidget(self.reset_button)
self.open_image_button = QPushButton("Open Image")
self.open_image_button.clicked.connect(self.open_image)
button_layout.addWidget(self.open_image_button)
self.save_button = QPushButton("Save Image")
self.save_button.clicked.connect(self.save_image)
button_layout.addWidget(self.save_button)
main_layout.addLayout(button_layout)
# Process initial image
self.process_image()
def process_image(self):
image_bgr = cv2.imread("image.png")
if image_bgr is None:
image_bgr = cv2.imread("default_image.png")
self.image_bgr = image_bgr
self.image_hsv = cv2.cvtColor(image_bgr, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
# Create initial mask using current slider values
lower_values = np.array([self.lower_h.value(), self.lower_s.value(), self.lower_v.value()])
upper_values = np.array([self.upper_h.value(), self.upper_s.value(), self.upper_v.value()])
mask_test = cv2.inRange(self.image_hsv, lower_values, upper_values)
image_bgr_masked = cv2.bitwise_and(image_bgr, image_bgr, mask=mask_test)
self.image_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(image_bgr_masked, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
self.update_image()
def update_image(self):
height, width, channel = self.image_rgb.shape
bytes_per_line = width * channel
q_image = QImage(self.image_rgb.data, width, height, bytes_per_line, QImage.Format.Format_RGB888)
pixmap = QPixmap.fromImage(q_image)
self.image_label.setPixmap(pixmap.scaled(700, 500, Qt.AspectRatioMode.KeepAspectRatio))
def update_hsv_range(self):
lower_values = np.array([self.lower_h.value(), self.lower_s.value(), self.lower_v.value()])
upper_values = np.array([self.upper_h.value(), self.upper_s.value(), self.upper_v.value()])
mask_test = cv2.inRange(self.image_hsv, lower_values, upper_values)
image_bgr_masked = cv2.bitwise_and(self.image_bgr, self.image_bgr, mask=mask_test)
self.image_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(image_bgr_masked, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
self.update_image()
def reset_values(self):
self.lower_h.setValue(50)
self.lower_s.setValue(100)
self.lower_v.setValue(50)
self.upper_h.setValue(130)
self.upper_s.setValue(255)
self.upper_v.setValue(255)
def open_image(self):
filename, _ = QFileDialog.getOpenFileName(self, "Select Image File", "", "Image Files (*.png *.jpg *.jpeg)")
if filename:
self.image_bgr = cv2.imread(filename)
if self.image_bgr is not None:
self.image_hsv = cv2.cvtColor(self.image_bgr, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
self.update_hsv_range() # This will apply current filter and update display
def save_image(self):
filename, _ = QFileDialog.getSaveFileName(self, "Save Image", "", "PNG Files (*.png);;JPEG Files (*.jpg)")
if filename:
# Make sure filename has an extension
if not filename.endswith(('.png', '.jpg', '.jpeg')):
filename += '.png'
# Convert and save
output_image = cv2.cvtColor(self.image_rgb, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
cv2.imwrite(filename, output_image)
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = MainWindow()
window.show()
sys.exit(app.exec())
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont
import os
# Font size and image dimensions
font_size = 88
width = 640
height = 480
# Use Symbola.ttf from current directory
font_path = "Symbola.ttf"
# Create image
img = Image.new('RGB', (width, height), color='white')
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
# Get font
font = ImageFont.truetype(font_path, font_size)
# Emoji matrix
emoji_matrix = [
['😀', '😁', '😂', '🤣', '😃'],
['😄', '😅', '😆', '😇', '😈'],
['😉', '😊', '😋', '😌', '😍'],
['😎', '😏', '😐', '😑', '😒']
]
# Calculate spacing
x_spacing = font_size + 10
y_spacing = font_size + 10
# Calculate starting position to center the grid
start_x = (width - (len(emoji_matrix[0]) * x_spacing)) // 2
start_y = (height - (len(emoji_matrix) * y_spacing)) // 2
# Draw emojis
for i, row in enumerate(emoji_matrix):
for j, emoji in enumerate(row):
x = start_x + (j * x_spacing)
y = start_y + (i * y_spacing)
draw.text((x, y), emoji, font=font, fill='black')
# Save the image
img.save('emoji_art.png')
print("Emoji art has been created successfully! Check emoji_art.png")
