You can download your free ebook from O'Reilly.
The Functional Programming in Python by David Mertz - publisher: O'Reilly - released: June 2015.
David Mertz is a director of the Python Software Foundation, and chair
of its Trademarks and Outreach & Education Committees. He wrote the
columns Charming Python and XML Matters for IBM developerWorks and the Addison-Wesley book Text Processing in Python. David has spoken at multiple OSCON and PyCon events.
This is the download link.
Is a blog about python programming language. You can see my work with python programming language, tutorials and news.
Saturday, March 19, 2016
Thursday, February 4, 2016
Testing PyQt4 under Python 3.5.1.
Today I working well with python 3.5.1.
Most of my source code was wrote with python 2.7 and the next step was to using pip3.5 to update and upgrade some python modules.
I try to install PyQt4 with pip3.5 - not working.
So I used the old way: whl file from here.
That was good, most of the scripts was running.
The main problem was OpenGL and that will make errors when you try to use QtOpenGL.
The result of this seam to me the python 3.5.1 it's now without OpenGL features.
Most of my source code was wrote with python 2.7 and the next step was to using pip3.5 to update and upgrade some python modules.
I try to install PyQt4 with pip3.5 - not working.
So I used the old way: whl file from here.
That was good, most of the scripts was running.
The main problem was OpenGL and that will make errors when you try to use QtOpenGL.
The result of this seam to me the python 3.5.1 it's now without OpenGL features.
The most short source code into Python 3.5.1 .
Just type this :
That will open your browser with one comics from xkcd website.
The antigravity module was added to Python 3.5.1. I'm not sure but seam working also with python 2.7 version.
import antigravity That will open your browser with one comics from xkcd website.
The antigravity module was added to Python 3.5.1. I'm not sure but seam working also with python 2.7 version.
Saturday, January 23, 2016
wmi python module - part 002.
According to MSDN Microsoft the Win32_Process WMI class represents a process on an operating system.
We can see all of the inherited properties of processes:
We can see all of the inherited properties of processes:
class Win32_Process : CIM_Process
{
string Caption;
string CommandLine;
string CreationClassName;
datetime CreationDate;
string CSCreationClassName;
string CSName;
string Description;
string ExecutablePath;
uint16 ExecutionState;
string Handle;
uint32 HandleCount;
datetime InstallDate;
uint64 KernelModeTime;
uint32 MaximumWorkingSetSize;
uint32 MinimumWorkingSetSize;
string Name;
string OSCreationClassName;
string OSName;
uint64 OtherOperationCount;
uint64 OtherTransferCount;
uint32 PageFaults;
uint32 PageFileUsage;
uint32 ParentProcessId;
uint32 PeakPageFileUsage;
uint64 PeakVirtualSize;
uint32 PeakWorkingSetSize;
uint32 Priority = NULL;
uint64 PrivatePageCount;
uint32 ProcessId;
uint32 QuotaNonPagedPoolUsage;
uint32 QuotaPagedPoolUsage;
uint32 QuotaPeakNonPagedPoolUsage;
uint32 QuotaPeakPagedPoolUsage;
uint64 ReadOperationCount;
uint64 ReadTransferCount;
uint32 SessionId;
string Status;
datetime TerminationDate;
uint32 ThreadCount;
uint64 UserModeTime;
uint64 VirtualSize;
string WindowsVersion;
uint64 WorkingSetSize;
uint64 WriteOperationCount;
uint64 WriteTransferCount;
}; import wmi
c = wmi.WMI()
for process in c.Win32_Process ():
name = process.Properties_("Name").Value
pid = process.Properties_('ProcessID').Value
parent = process.Properties_('ParentProcessId')
termination = process.Properties_('TerminationDate')
print (name,' = pid -',pid,'+', parent,'|termination_date-',termination) firefox.exe = pid - 13788 + 2564 |termination_date- None
explorer.exe = pid - 1048 + 772 |termination_date- None
sublime_text.exe = pid - 11404 + 2564 |termination_date- None
plugin_host.exe = pid - 7432 + 11404 |termination_date- None
cmd.exe = pid - 9568 + 2564 |termination_date- None
conhost.exe = pid - 14124 + 9568 |termination_date- None
conhost.exe = pid - 9700 + 11208 |termination_date- None
Taskmgr.exe = pid - 9424 + 13404 |termination_date- None
WmiPrvSE.exe = pid - 9764 + 772 |termination_date- None
SpfService64.exe = pid - 11908 + 684 |termination_date- None
python.exe = pid - 1308 + 9568 |termination_date- None
Posted by
Cătălin George Feștilă
Labels:
2016,
module,
python,
python 3,
python modules,
Spyder,
tutorial,
tutorials,
wmi
Friday, January 22, 2016
wmi python module - part 001.
Named WMI from Windows Management Instrumentation, this python module allow you to use Microsoft’s implementation of Web-Based Enterprise Management ( WBEM ).
Is a set of extensions to the Windows Driver Model AND that provides an operating system interface.
allows you to scripting languages like VBScript to manage Microsoft Windows personal computers and servers, both locally and remotely.
You cand read about this python module here.
Let try first example :
Now let's see another example can used by you with wmi python module.
This example let you see your processes.
I used the python version 3.3.5 and Spyder ( Scientific PYthon Development EnviRonment ) to test the script.
You can change .watch_for method args with: creation, deletion, modification or operation.
Is a set of extensions to the Windows Driver Model AND that provides an operating system interface.
allows you to scripting languages like VBScript to manage Microsoft Windows personal computers and servers, both locally and remotely.
You cand read about this python module here.
C:\Python34\Scripts>pip install wmi
...
Installing collected packages: wmi
Running setup.py install for wmi
warning: install_data: setup script did not provide a directory for 'readme.
txt' -- installing right in 'C:\Python34'
...
Successfully installed wmi
Cleaning up... Let try first example :
C:\Python34>python
Python 3.4.1 (v3.4.1:c0e311e010fc, May 18 2014, 10:45:13) [MSC v.1600 64 bit (AM
D64)] on win32
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> import wmi
>>> remote_process = wmi.WMI (computer="home").new ("Win32_Process")
>>> for i in wmi.WMI ().Win32_OperatingSystem ():
... print (i.Caption)
...
Microsoft Windows 10 Home Now let's see another example can used by you with wmi python module.
This example let you see your processes.
import wmi
import datetime
c = wmi.WMI()
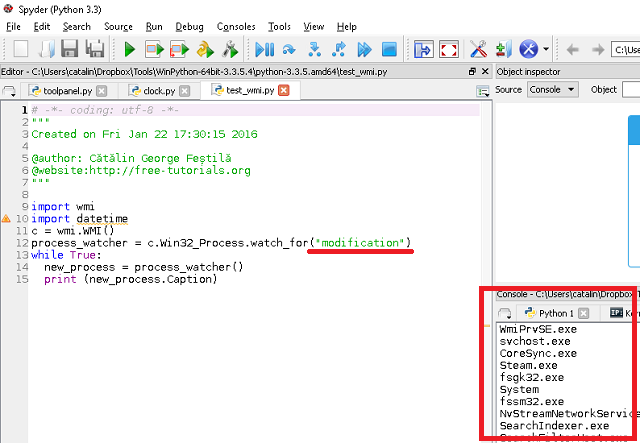
process_watcher = c.Win32_Process.watch_for("modification")
while True:
new_process = process_watcher()
print (new_process.Caption) I used the python version 3.3.5 and Spyder ( Scientific PYthon Development EnviRonment ) to test the script.
You can change .watch_for method args with: creation, deletion, modification or operation.

Posted by
Cătălin George Feștilă
Labels:
2016,
module,
python,
python 3,
python modules,
Spyder,
tutorial,
tutorials,
wmi
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)